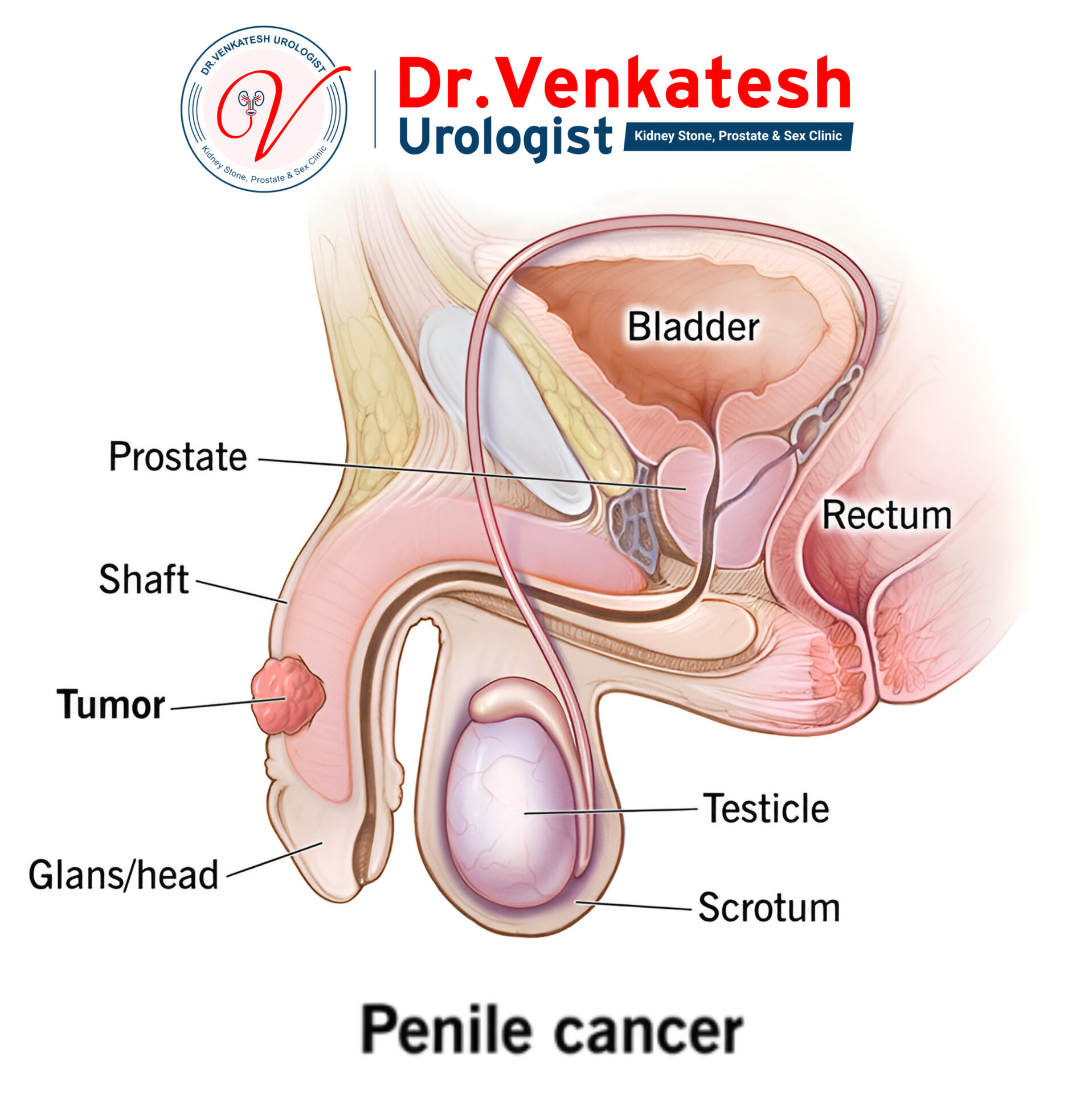
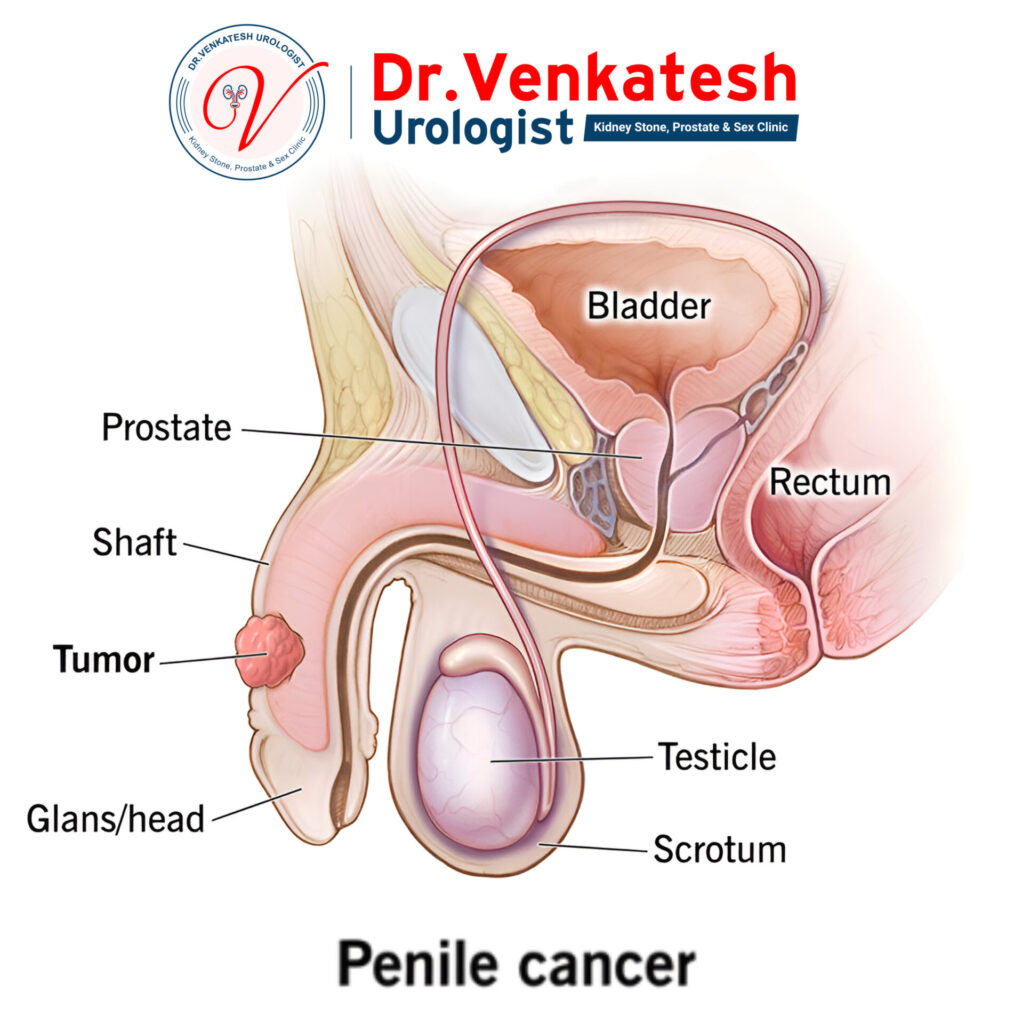
What is Penile Cancer?
Penile cancer occurs when malignant cells in the penis grow uncontrollably. The penis is a cylindrical reproductive organ that serves two primary functions: urination and sexual intercourse. Its main components include the shaft, which extends from the lower abdomen to the tip, known as the head or glans. In uncircumcised individuals, a layer of skin called the foreskin covers the glans. In contrast, circumcised individuals have the head of the penis exposed.
While cancer can develop anywhere within the penis, it most frequently originates in the glans or foreskin in those who are uncircumcised.
Dr. Venkatesh Kumar, a prominent Urologist, Sexologist, and Robotic Surgeon in Noida, specializes in diagnosing and treating penile cancer.
What Are the Types of Penile Cancer?
About ninety-five percent of penile cancers are classified as squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). This type of cancer originates in the outermost layer of skin known as the epithelium. Other, less common forms of penile cancer arise from different types of tissue:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): This cancer starts in the deepest layer of the epithelium. BCC is typically a slow-growing type of penile cancer.
- Melanoma: This cancer develops from melanocytes, the cells responsible for pigmentation in the skin. Melanoma is known to be a more aggressive form of cancer.
- Sarcoma: This type of cancer arises in muscle or connective tissue and is extremely rare among penile cancers.
Key Symptoms of Penile Cancer
Recognizing the symptoms of penile cancer early can significantly affect treatment success. Common symptoms include:
- Unusual Growths: Any new growth or sore on the penis that does not heal over time.
- Changes in Skin Color: Alterations in the color or texture of the skin on the penis, including patches that may appear white, red, or dark.
- Discharge: Unexplained discharge from the penis, often accompanied by a foul smell.
- Pain or Discomfort: Persistent pain or discomfort in the penis, especially in the presence of other symptoms.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Swelling in the groin or pelvic area, indicating possible spread to lymph nodes.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and timely intervention.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of penile cancer is not fully understood, several risk factors have been identified:
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection: Certain strains of HPV are linked to an increased risk of penile cancer.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is associated with various cancers, including penile cancer.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate cleaning of the penis can lead to the development of pre-cancerous lesions.
- Phimosis: A condition where the foreskin cannot be retracted, which may contribute to inflammation and cancer risk.
- Age: The risk of penile cancer increases with age, particularly in men over 60.
Understanding these risk factors can help in early detection and preventive measures.
Diagnosis of Penile Cancer
Diagnosis begins with a thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider. If cancer is suspected, the following diagnostic tests may be performed:
- Biopsy: A small sample of tissue is taken from the penis and examined for cancer cells.
- Imaging Tests: CT scans, MRI, or ultrasound may be used to determine if cancer has spread to other areas of the body.
- Blood Tests: To check for markers that may indicate cancer presence.
Timely diagnosis is vital for effective treatment planning.
Treatment Options for Penile Cancer
The treatment for penile cancer depends on the stage of cancer, its location, and the patient’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for penile cancer may involve the surgical removal of the tumor. This can range from a partial penectomy (removal of part of the penis) to total penectomy (removal of the entire penis) in severe cases.
- Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It may be used after surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells or as a primary treatment in early-stage cancer.
- Chemotherapy: In cases where the cancer has spread, chemotherapy may be administered to kill cancer cells throughout the body. This can be done in combination with surgery or radiation.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment helps the body’s immune system recognize and fight cancer cells. It may be an option for patients with specific types of penile cancer.
- Robotic Surgery: Dr. Venkatesh Kumar offers advanced robotic surgery options for lymph node dissection, which provide precision and minimally invasive techniques, leading to faster recovery times and reduced complications.
Preventive Measures
While not all cases of penile cancer can be prevented, certain measures can significantly reduce risk:
- Practice Good Hygiene: Regular washing of the genital area is essential, especially for uncircumcised men.
- Get Vaccinated: HPV vaccines can help protect against the strains of the virus that cause penile cancer.
- Avoid Tobacco Products: Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of various cancers.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular visits to a healthcare provider can help detect any early signs of penile cancer or other urological conditions.
Why Choose Dr. Venkatesh Kumar for Treatment?
Dr. Venkatesh Kumar is a distinguished Urologist and Robotic Surgeon based in Noida, renowned for his expertise in treating urological cancers. His compassionate approach and advanced surgical techniques ensure that patients receive the highest level of care. If you suspect you have symptoms of penile cancer or have any concerns, do not hesitate to contact Dr. Kumar for a consultation.
FAQs
- What are the early signs of penile cancer?
Early signs include unusual growths, changes in skin color, discharge, and persistent pain or discomfort. - Is penile cancer common?
Penile cancer is rare, but its incidence is increasing in some populations due to factors like HPV infection. - Can penile cancer be cured?
When detected early, penile cancer can often be treated successfully, leading to a good prognosis. - How can I reduce my risk of penile cancer?
Practicing good hygiene, quitting smoking, and getting vaccinated against HPV are effective preventive measures.
Conclusion
Penile cancer is a serious condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options can empower men to seek help early. Dr. Venkatesh Kumar is committed to providing expert care for patients dealing with penile cancer and other urological issues. If you have any concerns about your health, contact Dr. Kumar today for personalized care and support.