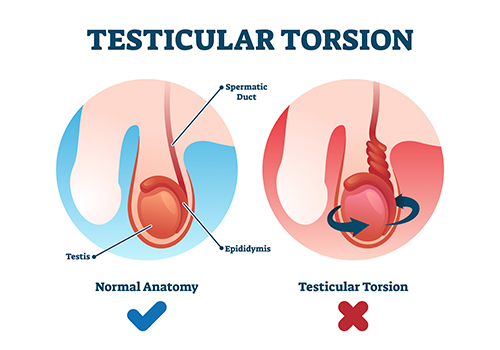
Testicular torsion usually occurs when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that carries the main blood supply to the testis This reduced blood flow is associated with sudden and often severe pain and swelling.
Testicular torsion usually occurs when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that carries the main blood supply to the testis This reduced blood flow is associated with sudden and often severe pain and swelling.
Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 18, but it can occur at any age, even before birth.
Emergency surgery is usually required for testicular torsion. If operated quickly, the testicle can usually be saved. If blood flow has been cut off for too long, a testicle might become so badly damaged that its removal may be necessary.
Symptoms usually start with sudden severe pain in scrotum with or without abdominal pain and swelling in the scrotum. It may progress to nausea, vomiting and even fever. On examination one testis may be higher up than the other.
Early recognition with immediate visit to urologist is of utmost importance in cases of testicular pain .
Recently a 18 year old boy presented in OPD with pain and swelling right testicle since 4 days . He visited local physician on day 1 of pain and was given some medicines without examination and advised warm compresses. Pain & swelling increased in severity over 3 days when he decided to consult urologist. Ultrasound scrotum revealed right testicular necrosis with absent blood flow and left testis normal.
Family was counselled about need for right orchidectomy (removal of right testis) & left orchidopexy ( fixation of left testis) . Intraoperatively right testis was blackened and despite detorsion & papaverine it was not salvageable and was removed.
Patient recovered well and was discharged on day 1 of surgery . Follow up visits were normal with wound healed well.

Take home message : Early recognition is important in cases of testicular pain and testicular torsion if treated in time can prevent loss of testis. Loss of testis at times can lead to inability to father a child ( male infertility).